|
People who just started to learn Spring framework is often confused by the term "Inversion of Control" (IoC) which can be achieved through "Dependency Injection" (DI). DI is a way of providing the dependencies (e.g. creating objects and its dependencies), wiring components into application. In Spring, those objects defined and instantiated by Spring containers then inject into application are called Spring Beans. IoC is a concept, it means to create instances of dependencies first, the concept is usually achieved by using metadata-driven approach to assemble instances at runtime. IoC is the end result of DI. However, DI is not the only way to achieve IoC. For example, Workday's XpressO is a great example of metadata-driven development to achieve IoC. Here are some more good explanations: Inversion of Control (IoC) means to create instances of dependencies first and latter instance of a class (optionally injecting them through constructor), instead of creating an instance of the class first and then the class instance creating instances of dependencies. Thus, inversion of control inverts the flow of control of the program. Instead of the callee controlling the flow of control (while creating dependencies), the caller controls the flow of control of the program. IoC is a programming technique, expressed here in terms of object-oriented programming, in which object coupling is bound at run time by an assembler object and is typically not known at compile time using static analysis. IoC is a common pattern in the Java community that helps wire lightweight containers or assemble components from different projects into a cohesive application. Spring helps in the creation of loosely coupled applications because of Dependency Injection.
0 Comments
One way to create thread is to pass a object that implements Runnable Interface to a Thread constructor as mentioned in Java Multithreading Approaches (Java Concurrency - Part 1): public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ Java Collection Framework (java.util.* package) is a unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections. This post is a quick note of my knowledge about Java Collection Framework that covers frequently used java data structure to store a group of elements and/or key-value pairs. In the java.util framework, there are two major camps - Collections & Map.
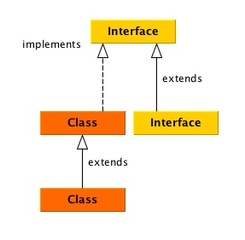
To illustrate, I use solid lines to denote 'extends', and dash lines to denote 'implements'. The way to use my note is to first go to the diagram looking for the specific class or interface, then read the brief blurb that'll remind you what the class or interface is about for the right data structure. Ever suspect your Java app leaking memory but not sure which class it is potentially causing OOM?
In this post, I recommend Eclipse Memory Analyzer (MAT) for developers to analyze heap dumps so you can chase down leak suspects. MAT is much easier to use and read than stand-along jhat unix command, and while monitor memory usage using VisualVM is helpful, MAT gives you specific hints about which classes may be the suspects. It is not uncommon that you need to watch the runtime performance of a Java application on a server. In this post, I'll show you how to set up a target JVM so you can monitor its cpu, heap memory, threads usage from a specific JMX client - VisualVM. VisualVM is similar to JConsole, a JMX-compliant monitoring tool, but is more advanced.
To use a JMX client, the setup you need to do first are:
With JMX agent enabled for a JVM, you can use a JMX Client (JConsole or VisualVM) to tap into your JVM to monitor its performance and memory usage at runtime. Your java runtime is not enabled with JMX by default unless you explicitly specify to turn it on.
With regards to java concurrency, when reading some API documentation (e.g. java.util.concurrent), there's the term "non-blocking" and "blocking." In computer science, non-blocking means:
In Java concurrency, ForkJoinPool uses a work-stealing multi-threading framework which works well for executing tasks of uneven distribution of chunk sizes. Before you read on, you need to know Java Multithreading Approaches first.
A ForkJoinPool implements ExecutorService but it differs from other (I'll refer them as 'traditional') ExecutorService mainly by virtue of employing work-stealing - all threads in the pool attempt to find and execute subtasks created by other active tasks. It automatically balance the task load between threads, while traditional ThreadPoolExecutor has no mechanism for such kind of load balancing. If no available worker thread is available, tasks will be blocked until a thread becomes available to steal work from those workers who are busy. In Java concurrency, there are two low level concurrency implementations in Java to create a thread - extend the Thread class or implement Runnable interface. These basic approaches neither return value from the thread nor throw exception should anything goes wrong. There's a third approach since Java 1.5 - use Java Concurrency package which supports to receive return values from thread execution.
Before I go into WeakHashmap, first let's look at different types of reference-object. A reference object encapsulates a reference to some other object. There are different level of reachability of references, from the strongest to the weakest. The weaker the reference, the more likely it is to be thrown away.
|
Categories
All
Archives
May 2020
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed