
Queue and Stack are basic data structure. This post is about implementing Breadth First Search (BFS) & Depth First Search (DFS) using concept of Queue and Stack.
0 Comments
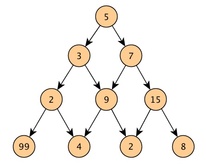 Assuming we have a set of values (see left). If you write these values down on a a piece of paper, from the top element you can branch downward into either left or right element each has its value. You can get a set of values with triangular look as shown. The question is, going from the value at the top to the bottom by choosing to go down the path of either left or right, what is the maximum sum among all possible paths?  Tail recursive saves stack memory. A recursive function is said to be tail-recursive if there is nothing to do after the function returns except returning its value. In this case, instead of allocating a stack frame for each call, the compiler can rework the code to simply reuse the current stack frame, meaning a tail-recursive function will only use a single stack frame as opposed to hundreds or even thousands of stack frame as in the case of regular recursive calls. Also, in a tail-recursive case, with each evaluation of the recursive call, the solution (e.g., a running total) is updated through parameter. A smart compiler can make Tail Recursion as efficient as iteration normally is. We'll see an tail-recursion implementation of Fibonacci at the end of this post. Using Fibonacci as an example, a Fibonacci sequence: [f(0)...f(n)]=[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ...] The Dijkstra's Algorithm (shortest route) finds the shortest distance and path from a source to all destination in a directed graph which is defined by a set of vertexes (V) and a collection of edges.
I found the easiest way to understand how Dijkstra's algorithm works is to take a look at this visual explanation below: |
Categories
All
Archives
May 2020
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed